פּראָדוקטן קאַטעגאָריע
- FM טראַנסמיטער
- קסנומקס-קסנומקסוו קסנומקסוו-קסנומקסוו קסנומקסקוו-קסנומקסקוו קסנומקסקוו, +
- טעלעוויזיע טראַנסמיטער
- קסנומקס-קסנומקסוו קסנומקס-קסנומקסקוו קסנומקסקוו-קסנומקסקוו
- FM אַנטענאַ
- טעלעוויזיע אַנטענע
- אַנטענאַ אַקסעססאָרי
- קאַבלע קאַנעקטער מאַכט ספּליטטער דאַמי לאָוד
- רף טראַנסיסטאָר
- פּאָווער סופּפּלי
- אַודיאָ עקוויפּמענץ
- דטוו Front סוף עקוויפּמענט
- לינק סיסטעם
- סטל סיסטעם מייקראַווייוו לינק סיסטעם
- FM ראַדיאָ
- מאַכט מעטער
- אנדערע פּראָדוקטן
- ספּעציעלע פֿאַר קאָראָנאַווירוס
פּראָדוקטן טאַגס
פמוסער זייטלעך
- es.fmuser.net
- it.fmuser.net
- fr.fmuser.net
- de.fmuser.net
- af.fmuser.net -> אפריקאנס
- sq.fmuser.net -> אַלבאַניש
- ar.fmuser.net -> אַראַביש
- hy.fmuser.net -> ארמאניש
- az.fmuser.net -> אַזערביידזשאַניש
- eu.fmuser.net -> באַסקיש
- be.fmuser.net -> בעלאָרוסיש
- bg.fmuser.net -> בולגאַריש
- ca.fmuser.net -> קאַטאַלאַניש
- zh-CN.fmuser.net -> כינעזיש (סימפּליפיעד)
- zh-TW.fmuser.net -> כינעזיש (טראַדיציאָנעל)
- hr.fmuser.net -> קראָאַטיש
- cs.fmuser.net -> טשעכיש
- da.fmuser.net -> דאַניש
- nl.fmuser.net -> האָלענדיש
- et.fmuser.net -> עסטיש
- tl.fmuser.net -> טאַגאַלאָג
- fi.fmuser.net -> פֿיניש
- fr.fmuser.net -> פראנצויזיש
- gl.fmuser.net -> גאליציאנער
- ka.fmuser.net -> גרוזיניש
- de.fmuser.net -> דייַטש
- el.fmuser.net -> גריכיש
- ht.fmuser.net -> Haitian Creole
- iw.fmuser.net -> העברעיש
- hi.fmuser.net -> הינדיש
- hu.fmuser.net -> אונגעריש
- is.fmuser.net -> איסלענדיש
- id.fmuser.net -> אינדאָנעזיש
- ga.fmuser.net -> איריש
- it.fmuser.net -> איטאַליעניש
- ja.fmuser.net -> יאַפּאַניש
- ko.fmuser.net -> קאָרעיִש
- lv.fmuser.net -> לעטיש
- lt.fmuser.net -> ליטוויש
- mk.fmuser.net -> מאַקעדאניש
- ms.fmuser.net -> מאַלייַיש
- mt.fmuser.net -> מאלטעזיש
- no.fmuser.net -> נאָרוועגיש
- fa.fmuser.net -> פּערסיש
- pl.fmuser.net -> פויליש
- pt.fmuser.net -> פּאָרטוגעזיש
- ro.fmuser.net -> רומעניש
- ru.fmuser.net -> רוסיש
- sr.fmuser.net -> סערביש
- sk.fmuser.net -> סלאָוואַקיש
- sl.fmuser.net -> סלאוועניש
- es.fmuser.net -> שפּאַניש
- sw.fmuser.net -> סוואַהילי
- sv.fmuser.net -> שוועדיש
- th.fmuser.net -> טייַלענדיש
- tr.fmuser.net -> טערקיש
- uk.fmuser.net -> אוקראיניש
- ur.fmuser.net -> אורדו
- vi.fmuser.net -> וויעטנאַמעזיש
- cy.fmuser.net -> וועלש
- yi.fmuser.net -> ייִדיש
איין פרעקווענסי נעטוואָרק (SFN) & DAB
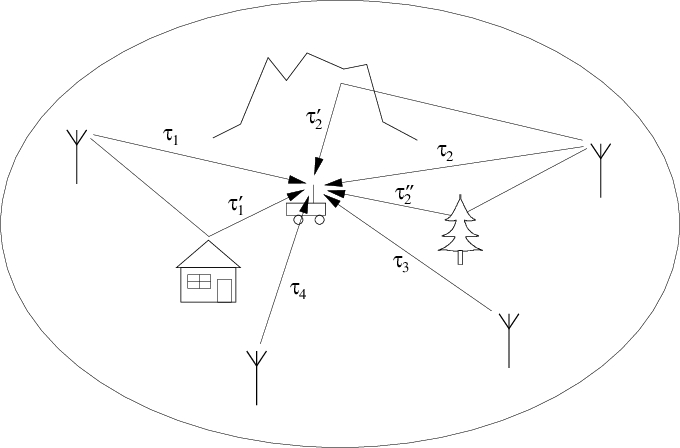
SFN - Single Frequency Network
A Single Frequency Network (SFN) is a network of transmitting stations that use the same frequency to transmit the same information. A Single Frequency Network is a means to extend the coverage area without the use of additional frequencies.
An SFN is particularly interesting for broadcasting. Both T-DAB (digital radio via terrestrial transmitters) and DVB-T (digital television via terrestrial transmitters) have the possibility for a single frequency network. An SFN can be used with other radio communication systems, such as wireless local area networks as well.
The SFN is based on the use of Coded Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (COFDM). COFDM has the advantage that it is very robust against reception of a signal together with echoes of the same signal (multipath reception). This robustness against multipath reception is obtained through the use of a 'guard interval'. This is a proportion of the time there is no data transmitted between the symbols. This guard interval reduces the transmission capacity.
This multipath immunity can be used to build a SFN with an overlapping network of transmitter stations which use the same frequency. In the areas of overlap, the weaker of the two signals is considered as an echo due to multipath reception. However, the echo has to fall within the guard interval and the stations must be synchronized. Hence, if two stations are far apart, the time delay between the two signals can be large and the system will need a large guard interval.
This extension of the coverage area does not come for free. Drawbacks of a SFN are:
the guard interval reduces the capacity;
there is no option for local variations in programming;
the transmitting stations must be synchronized.
אָנפּעטשלען
Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) is a digital radio system that is designed to replace the analogue radio. The benefits of DAB above analogue FM-radio are:
Better sound quality;
Better mobile reception;
Easy program selection;
Advanced programme associated data;
Possibilty for information and data services.
To receive DAB a new DAB radio is needed.
T-DAB and S-DAB
In the first place, DAB is broadcast on terrestrial networks. Therefore it is sometimes called T-DAB; Terrestrial DAB. A satellite version (S-DAB) is developed later.
Eureka 147
The development of DAB started in 1987 as a European Project, the Eureka 147 Project. The Project merged in 1999 with the WorldDAB Forum (formerly the EuroDAB Forum). Since 2000, the WorldDAB Forum is responsible for the technical maintenance of the EU-147 DAB standard.
Multimedia services
DAB can also be used for the deliverance of other services. DAB has two additions to the standard for the deliverance of IP packets (DAB IP) and for the deliverance of multimedia services (DMB).
דווב-ג
Digital Video Broadcasting - Terrestrial (DVB-T) is a system for broadcasting of digital television via terrestrial transmitters. DVB-T is part of the family of standards of the DVB Project. As all other DVB standards, DVB-T is based on the transmission of data containers. The DVB-T system uses the same 8 MHz (or 7 or 6 MHz) radio-channels as used for analogue television.
These containers carry a flexible combination of MPEG-2 video, audio and data. The container can contain more than one television program as well as radio programs or data services. The data of the different programs are combined in a so-called multiplex. Each container carries Service Information (SI) which gives details about the programmes being broadcast. Each analogue television channel of 8 MHz can be used to transmit about 3-6 television programs.
To receive DVB-T an decoder or set-top-box is needed. The decoder receives the signal and decodes the compressed video to a signal suitable for an ordinary television.
DVB-T transmission
The transmission is based on Coded Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (COFDM). COFDM uses a large number of carriers. Each of these carriers is used to transmit only a portion of the total amount of data. The data is modulated on the carriers with QPSK or QAM. COFDM has the advantage that it is very robust against multipath reception and frequency selective fading. This robustness against multipath reception is obtained through the use of a 'guard interval'. This is a proportion of the time there is no data transmitted. This guard interval reduces the transmission capacity.
Because of this multipath immunity, it is possible to extend the coverage area with the use of an overlapping network of transmitter stations which use the same frequency, a so-called single frequency network (SFN). In the areas of overlap, the weaker of the two signals is considered as an echo due to multipath reception. However, the stations have to be synchronized and the echo has to fall within the guard time. Hence, if two stations are far apart, the time delay between the two signals can be large and the system will need a large guard interval.
There are two COFDM transmission modes possible in the DVB-T system. A 2k mode which uses 1705 carriers and a 8k mode which uses 6817 carriers. The 2k mode is suitable for single transmitter operation and for relatively small single frequency networks with limited transmission power. The 8k mode can be used both for single transmitter operation and for large area single frequency networks. The guard interval is selectable.
Portable and mobile reception of DVB-T signals is possible. It is even possible to mix the reception modes by using hierarchical transmissions, in which one of the modulated streams (so-called HP – High Priority stream), is given a higher protection against errors, to make is suitable for mobile reception; while the other one (so-called LP – Low Priority stream), has a lower protection. The higher protection mode will have a lower net bit rate available.
From DVB-T is also a variant developed, DVB-H, that is optimized for mobile reception on handheld portables.
אויב איר וואָלט ווי צו בויען אַ ראַדיאָ סטאַנציע, בוסט דיין עפעם ראַדיאָ טראַנסמיטער אָדער דאַרפֿן קיין אנדערע עפעם ויסריכט, ביטע פילן פֿרייַ צו קאָנטאַקט אונדז: [אימעיל באשיצט].

